Halogens Nitro
Fluro NO2 Nitro
Chloro
Bromo
Ido
Properties of halogenated: F Cl Br I are insoluble in water, F is nonreactive (Teflon)
Properties of nitro compounds: insoluble in water, unreactive to chemical attack except under drastic conditions, tend to be explosive (TNT), pleasant odour

Alcohols
have an O-H added to the compound
the ending changes from ane to anol
Properties: soluble (except C-H chain), poisonous

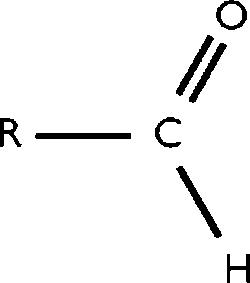
Aldehyde
double bonded oxygen at the end of the chain
the ending changes from ane to al
Keytone
double bonded oxygen added to the middle of a chain
the ending changes from ane to one
Properties:
soluble in water, aldehydes (very reactive) =>carboxylic acids, Keytones are relatively unreactive